AngularJS filter ngOptions
▌Introduction
$filter is one of the most useful
service in angular. There some filter components already defined in angular. In
this sample, I would like to show how to use $filter for displaying different options
of ngOptions which depends on
another directive.
▌Environment
▋ AngularJS 1.5.8
▋ Sweet Alert 1.1.3
▌Implement
▋Goal
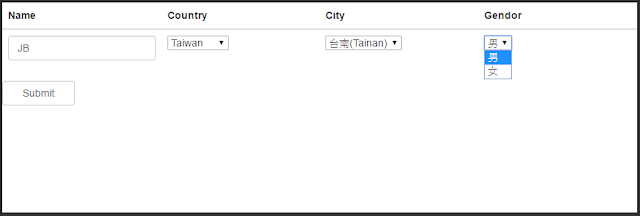
We will initialize all the data for ngOptions in the following drop-down-boxes.
1. Country
1. Country
2. City
3. Gender
However, the options of City and Gender will be changed due to the
selected value of Country. We will get this done by using $filter.
▋JS : Controller
angular.module('app', [])
.factory('optionFactory', function () {
var factory = [];
factory.getGenders = function () {
var data = [{
'id': 1,
'nameEN': 'male',
'nameZH': '男',
'nameJP': 'マン'
}, {
'id': 2,
'nameEN': 'female',
'nameZH': '女',
'nameJP': 'おんな'
}];
return data;
};
factory.getCountries = function () {
var data = [{'id': 1,'name': 'Taiwan','local': 'ZH'}, {'id': 2,'name': 'American','local': 'EN'}, {'id': 3,'name': 'Japan','local': 'JP'}];
return data;
}
factory.getCities = function () {
var data = [{'id': 1,'name': '台北(Taipei)','countryId': 1}, {'id': 2,'name': '台南(Tainan)','countryId': 1}, {'id': 3,'name': 'New York','countryId': 2}, {'id': 4, 'name': 'Chicago','countryId': 2}, {'id': 5,'name': 'Houston','countryId': 2}, {'id': 6, 'name': 'とうきょうと(Tokyo)','countryId': 3}, {'id': 7,'name': 'きょうとふ(Kyoto)', 'countryId': 3}];
return data;
}
return factory;
})
.controller('DemoCtrl', function ($scope, $filter,
optionFactory) {
$scope.genderOptions = optionFactory.getGenders();
$scope.countryOptions = optionFactory.getCountries();
$scope.cityOptions = optionFactory.getCities();
$scope.showResult = function () {
//Show something…
}
})
|
Okay, the above codes will result in showing all the options in
drop-down-box: City, and the default options of Gender are always displayed
with English.
Let’s start to update the codes with $filter!
▋Filter for City
▋Create filter
angular.module('app', [])
.filter('cityFilter', function () {
return function (cities, selectedCountryId)
{
var filtered = [];
angular.forEach(cities, function (city) {
if (city.countryId ===
selectedCountryId) {
filtered.push(city);
}
});
return filtered;
};
})
|
▋Put filter to ngOptions
<select ng-options="city.name for city in (cityOptions | cityFilter:my.country.id)" ng-model="my.city" />
|
So the filter will ignore the cities which not belong to the selected country!
▋Filter for Gender
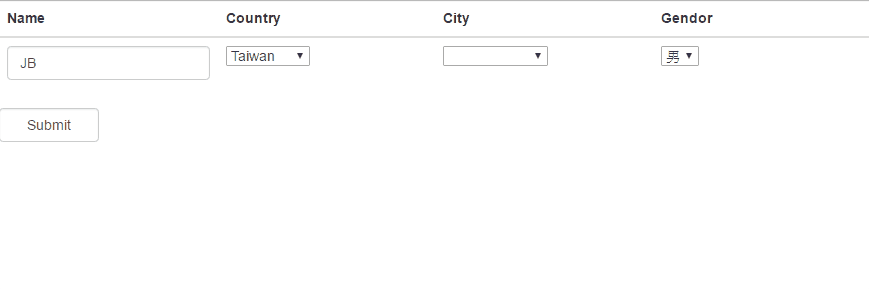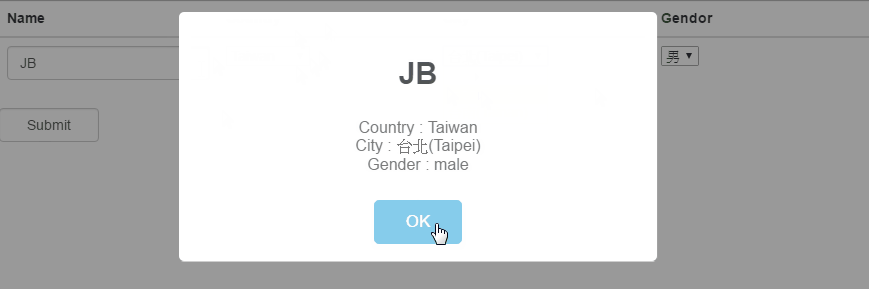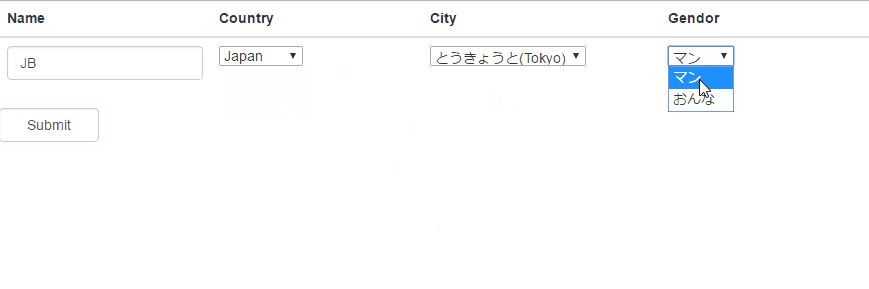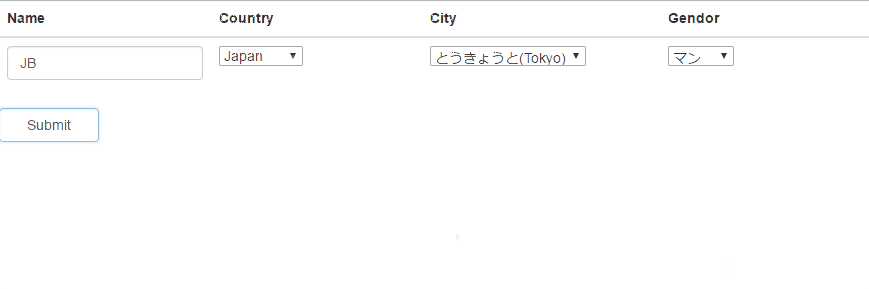
Another use of Filter
is changing the display value from original value.
In this sample, we want to
show the different localization wording for gender options.
Fortunately, we had kept the
Traditional Chinese, English and Japanese wordings in the original gender
array.
var data = [{'id': 1,'nameEN': 'male','nameZH': '男','nameJP':
'マン'}, {'id': 2,'nameEN': 'female', 'nameZH': '女','nameJP':
'おんな'}];
So all we have to do is
passing the selected country’s corresponding localization to Filter, and let
the filter return the correct wording for us!
▋Create filter
angular.module('app', [])
.filter('genderFilter', function () {
return function (gender, local) {
var converted = "";
switch (local) {
case "ZH":
converted = gender.nameZH;
break;
case "JP":
converted = gender.nameJP;
break;
case "ZH":
default:
converted = gender.nameEN;
break;
}
return converted;
}
})
|
▋Put filter to ngOptions
<select ng-options="gender as (gender|genderFilter:my.country.local) for gender in genderOptions" ng-model="my.gender" />
|
We used the
benefit of “select as …” and put the filter inside for returning the
corresponding wording of gender.
▋Final result